Today, we’re excited to announce the general availability of our new organization and enterprise-level security overview dashboards, alongside enhanced secret scanning metrics and the enablement trends reports. These features are designed to provide comprehensive insights, improved prioritization, and advanced filtering options to streamline your security improvements.
Code security insights
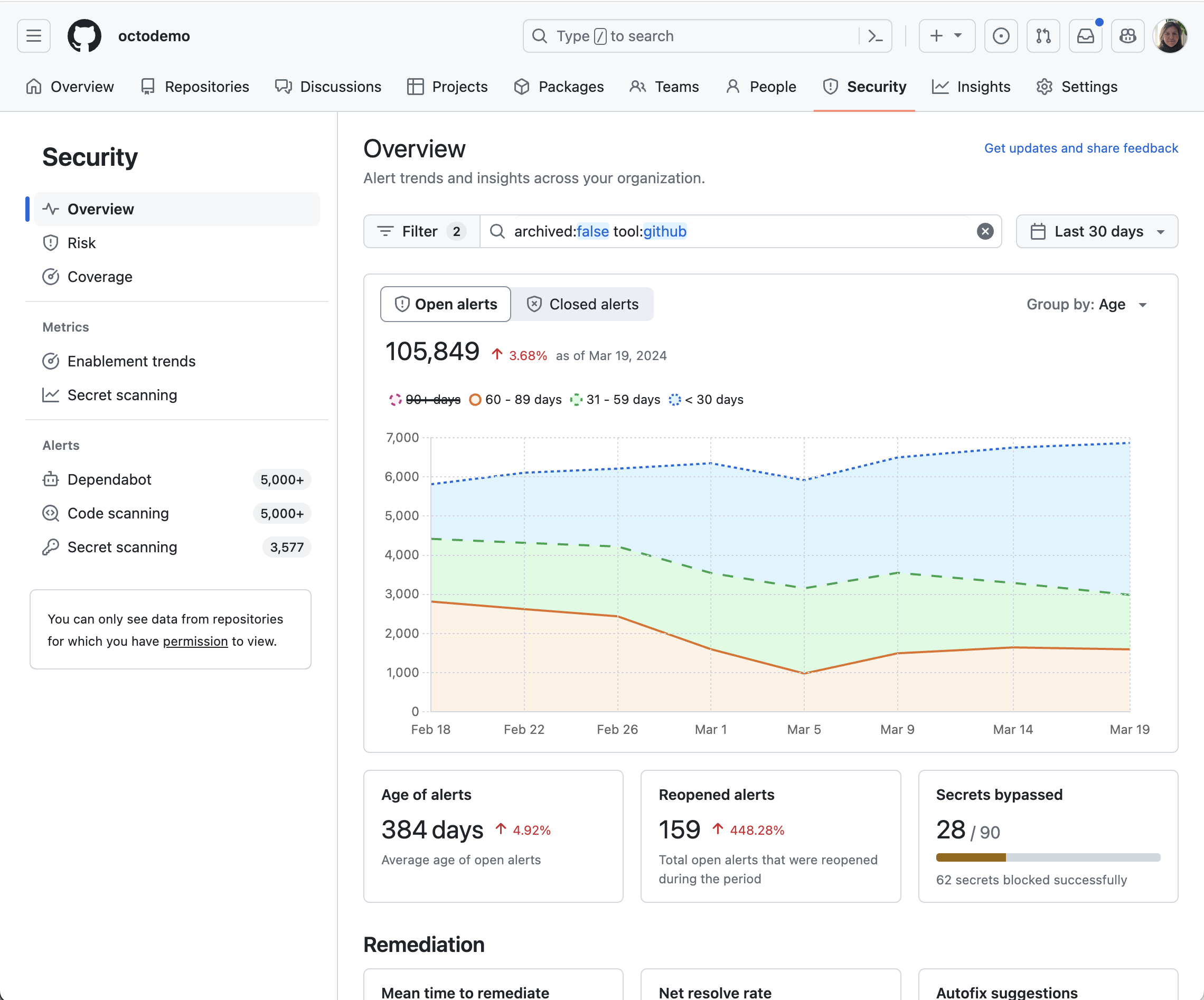
Our new security overview dashboard, available at both the organization and enterprise levels, integrates security into the core of the development lifecycle. This empowers you to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities. Key features include:
- Track security improvements: Monitor trends over time by age, severity, and security tool, simplifying prioritization with top 10 lists focused on repositories and advisories.
- Autofix impact: Understand how autofix, powered by GitHub Copilot, is influencing your enterprise’s security remediation efforts.
- Advanced filtering: Customize data focus with filters by attributes such as team, repository metadata (i.e., custom repository properties), and security tool-specific filters:
- Dependabot: Filter by ecosystem, package, and dependency scope.
- CodeQL/Third-Party: Filter by specific rules.
- Secret Scanning: Filter by secret type, provider, push protection status, and validity.
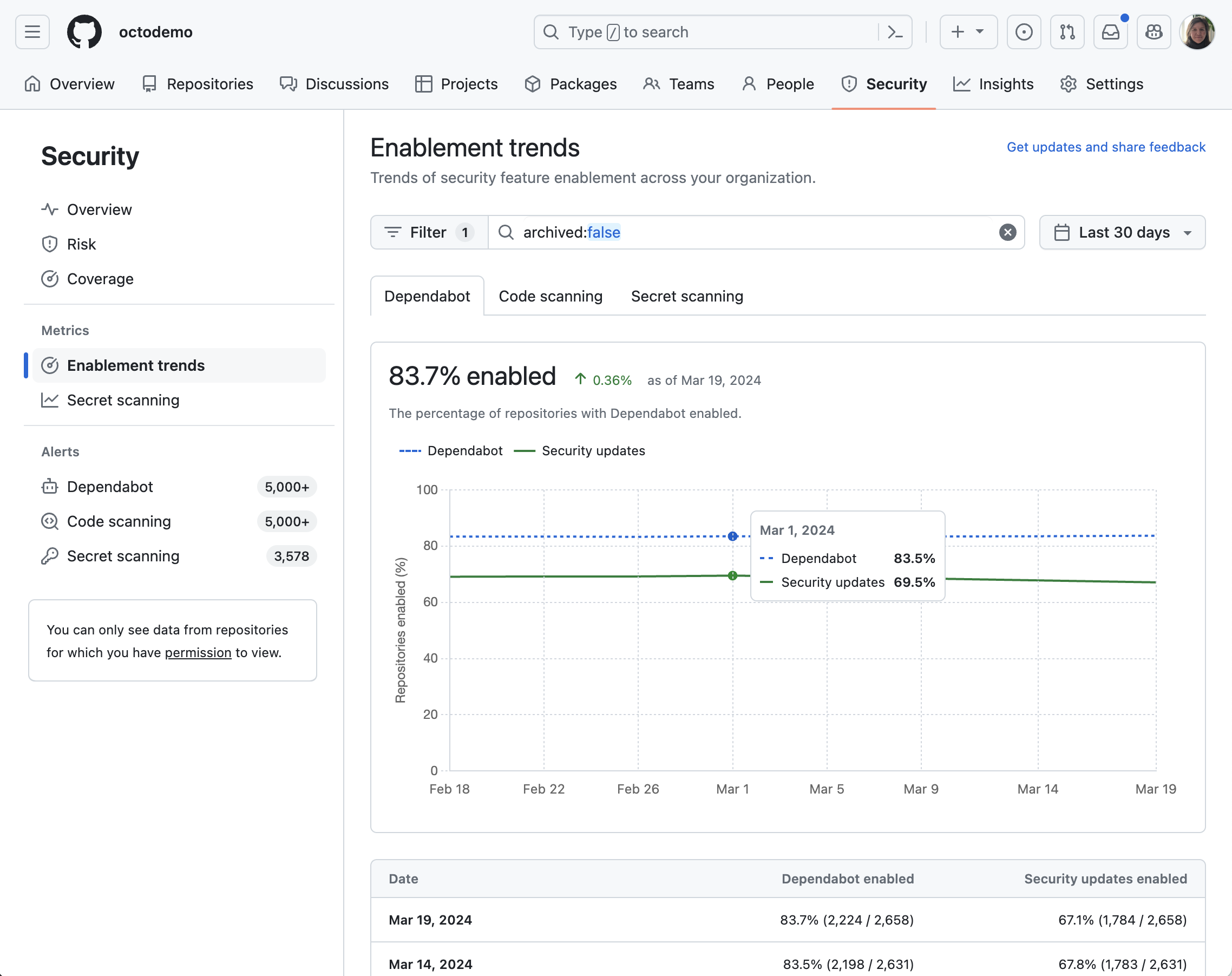
Monitor the enablement trends of all security tools with detailed insights into the activation status of Dependabot alerts, Dependabot security updates, code scanning, secret scanning alerts, and secret scanning push protection, giving you at-a-glance oversight of your security coverage.
Push protection insights for secret scanning

Gain insights into how push protection is functioning throughout your enterprise. Monitor the number of pushes containing secrets that have been successfully blocked, as well as instances where push protection was bypassed. Detailed insights by secret type, repository, and reasons for bypassing are also available.
To access these features, navigate to your profile photo in the top-right corner of GitHub.com and select the organization or enterprise you wish to view. For organizations, click on the Security tab. For enterprises, click Code Security in the enterprise account sidebar.
These features are generally available on GitHub.com today and will be generally available in GitHub Enterprise Server 3.14.
Learn more about the security overview dashboard, the secret scanning metrics report and the enablement trends report

