Work with GitHub Actions in your terminal with GitHub CLI
gh brings GitHub to the command line by helping developers manage pull requests, issues, gists, and much more. As of 1.9.0, even more of GitHub is available in your terminal:…
gh brings GitHub to the command line by helping developers manage pull requests, issues, gists, and much more. As of 1.9.0, even more of GitHub is available in your terminal: GitHub Actions.
It’s already possible to make great things using gh from within GitHub Actions as Mislav shared in his recent blog post. Now, you can get insight into workflow runs and files from the comfort of your own local terminal with two new top-level commands: gh run and gh workflow.
Getting insight into workflow runs
Despite our best efforts to write code that is good and true, builds sometimes fail. It’s possible to get quick insight into what might be failing for an open pull request with gh pr checks, but this doesn’t help with understanding workflow runs across an entire repository. With the new gh run list, you receive an overview of all types of workflow runs whether they were triggered via a push, pull request, webhook, or manual event.

We’ve made it easier to stay on top of in-progress workflow runs with gh run watch, which you can use to either follow along as a workflow run executes or combine with other tools to alert you when runs are finished. Combining gh run watch with, on Ubuntu, a command like notify-send means more time to wander off from your keyboard and do something like pet a cat or gaze at a plant.

…and when the run is done:

To drill down into the details of a single run, you can use gh run view, optionally going into as much detail as the individual steps of a job. For example, you might want to know why the linter failed on some code:
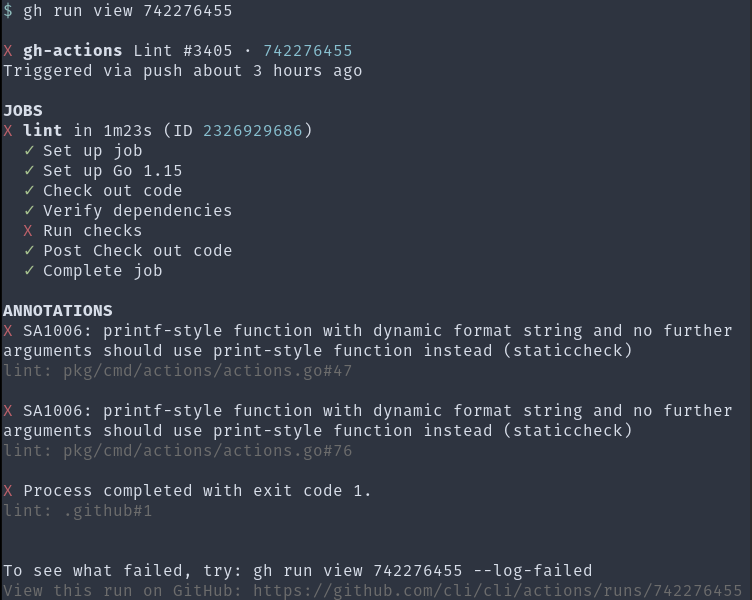
For more mysterious failures, you can combine a tool like grep with gh run view --log to search across a run’s entire log output. This can help you debug failures across a build matrix. For example, I can see here that panic is happening on Ubuntu and MacOS but not on Windows:

If --log is too much information, gh run --log-failed will output only the log lines for individual steps that failed. This is great for getting right to the logs for a failed step instead of having to run grep yourself. To illustrate, here I’m using --log-failed to only see the log output for a step that failed instead of the log output for every step:

gh run also knows about artifacts generated during a workflow run and can help discover and retrieve them.
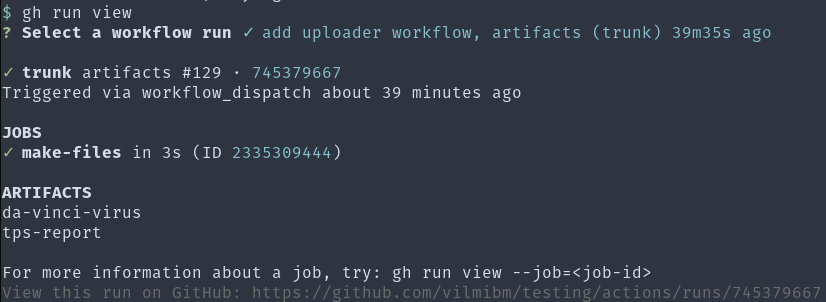
To download artifacts, you can select them by name with gh run download -n tps-report or via an interactive selector:

Finally, if you suspect that a run might be failing intermittently or just really like to watch things fail, you can now rerun runs without leaving your terminal using gh run rerun:

It’s easier to manage workflow files too
Runs in GitHub Actions are defined by workflow files in YAML format living in .github/workflows in your repository. A workflow file describes a workflow’s name, behavior, and what types of events cause the workflow to be run.
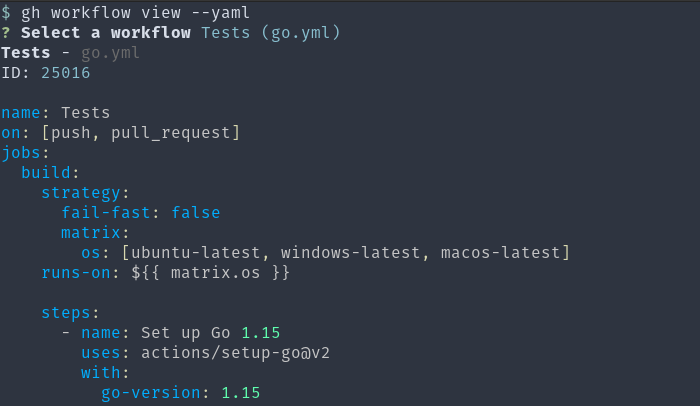
With gh workflow view, you can get a summary of a workflow’s recent runs to help ensure it’s doing what you want. To remind yourself what a workflow does, gh workflow view --yaml will print it out, complete with pretty colors.

Sometimes workflows are broken or are works in progress. To conveniently manage them without having to remove them entirely from your repository, you can now use gh workflow enable and gh workflow disable:

While many workflow runs are triggered by pull requests or pushed branches, it’s possible to have a workflow file run on command using a workflow_dispatch event.
You might want to run a workflow on command to perform cleanup tasks in a repository or perhaps set a workflow for manual dispatch while it’s still a work in progress. Workflows that support this event can now be triggered from your command line with gh workflow run, making it more convenient to work with and script workflow_dispatch workflows.
To see how gh workflow run can help with workflow file development, I’ll show an example of how it can fit into your toolchain. I want to run some automation on incoming pull requests to ensure they meet certain criteria. Here’s a workflow file called pr-check.yml that checks if incoming pull requests have a body:
name: Pull Request Check
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
body:
default: ""
test:
default: "false"
pull_request_target:
jobs:
check-body-length:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: check
env:
PRNUM: ${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}
PRBODY: ${{ github.event.pull_request.body }}
TESTBODY: ${{ github.event.inputs.body }}
TEST: ${{ github.event.inputs.test }}
run: |
if [ "$TEST" = "true" ]
then
PRBODY=$TESTBODY
fi
commentPR () {
if [ "$TEST" = "true" ]
then
echo "would comment: '${1}'"
else
gh pr comment $PRNUM -b "${1}"
fi
}
if [ "$PRBODY" = "" ]
then
commentPR "Thanks! Please add a body so we can better review your contribution."
fi
It responds to both pull_request_target and workflow_dispatch, meaning it will run whenever a pull request opens on my repository or when I manually invoke it.
When invoked manually, it accepts a test input that allows for a mock pull request body to be checked. I can run it like this:
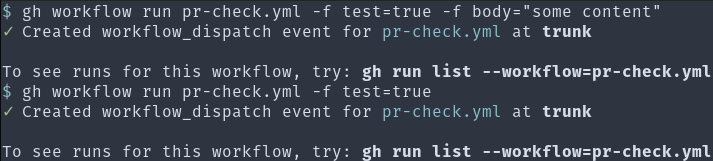
I can check the output of gh run view --log to ensure that the code behaved as expected. Since I’m on the command line, this process can be further scripted or streamlined with aliases.
Being able to programmatically run this workflow right from my terminal as I work makes me feel better about modifying the if [ $PRBODY = true ] conditional to do more complex things.
Let us know what you think
Let us know what you come up with using gh run and gh workflow in our Discussion forum! We’re excited to iterate on this new integration, and are eager for feedback. Are you new to the GitHub CLI? Install it today.
In the future, we hope to make it even easier to author and deploy workflow files, but for now we hope you enjoy everything that’s new in GitHub 1.9.0.
Tags:
Written by
Related posts

From pair to peer programmer: Our vision for agentic workflows in GitHub Copilot
AI agents in GitHub Copilot don’t just assist developers but actively solve problems through multi-step reasoning and execution. Here’s what that means.

GitHub Availability Report: May 2025
In May, we experienced three incidents that resulted in degraded performance across GitHub services.

GitHub Universe 2025: Here’s what’s in store at this year’s developer wonderland
Sharpen your skills, test out new tools, and connect with people who build like you.