How to start using reusable workflows with GitHub Actions
Reusable workflows offer a simple and powerful way to avoid copying and pasting workflows across your repositories.
From automating repetitive tasks to building continuous integration and continuous deployment pipelines, you can do a lot with GitHub Actions.
But until recently, you had to copy and paste YAML files from one repository to another if you wanted to use them in more than one place.
Enter reusable workflows, which officially launched in 2021 and offer a simple and powerful way to avoid copying and pasting workflows across your repositories.
Below, I’ll go over some of the benefits of reusable workflows and how to use them. I’ll also talk through how reusable workflows are different from composite actions and some current limitations.
What are the benefits of using reusable workflows?
- Reusable workflows are … reusable. Reusable workflows let you DRY (don’t repeat yourself) your Actions configurations, so you don’t need to copy and paste your workflows from one repository to another.
Case in point: if you have three different Node applications and you’re building them all the same way, you can use one reusable workflow instead of copying and pasting your workflows again and again.
- Reusable workflows can enforce context consistency across environments. When combined with OpenID Connect, reusable workflows allow you to require certain tests to be run before code can be deployed to production.
Let’s say, for example, that you have a cloud-hosted database and your applications are going to run database migrations when they’re deployed. You can put a policy in front of that database requiring that a specific reusable workflow is used before any deployment.
How to make any GitHub Actions workflow reusable
Step 1: Add a workflow_call trigger
A reusable workflow is just like any GitHub Actions workflow with one key difference: it includes a workflow_call trigger.
That means all you need to do is add in the following syntax to any action’s YAML workflow file:
on:
workflow_call:
You can then reference this workflow in another workflow by adding in this syntax:
Uses:
USER_OR_ORG_NAME/REPO_NAME/.github/workflows/REUSABLE_WORKFLOW_FILE.yml@TAG_OR_BRANCH
You can also pass data such as job information or passwords to a reusable workflow by using inputs and secret triggers. Inputs are used to pass non-sensitive information while secrets are used to pass along sensitive information such as passwords and credentials. You can learn more about that in our docs.
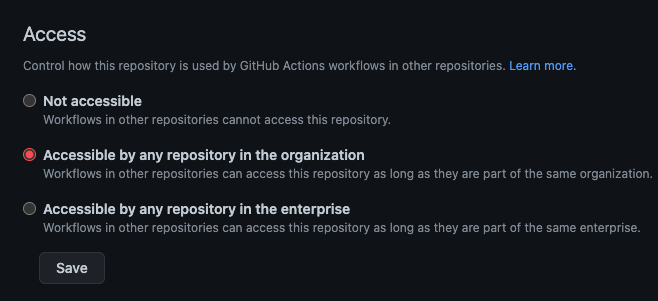
Step 2: Make your actions accessible across your organization
After you add a workflow_call trigger, you need to make sure that your repositories in your organization have access to it. To do this, go to your repository settings, select Actions, and enable access to repositories in your organization.
Some limitations with reusable workflows
There are some limitations with reusable workflows. I want to call out a few to keep in mind:
- You can’t reference a reusable workflow that’s in a private repository. If you have a reusable workflow in a private repository, only other workflows in that private repository can use it.
-
Reusable workflows can be nested. From within a reusable workflow you can call another reusable workflow and you can connect up to four levels of workflows.
Reusable workflows vs. composite actions
When we launched reusable workflows, one of the first questions we got was around how they’re different from composite actions.
For the uninitiated, composite actions enable you to combine multiple actions into a single action that you can then insert into any workflow. This means you can refactor long YAML workflow files into much smaller files—and you can also save yourself a fair amount of copying and pasting. Plus, if something like your credentials change, you won’t have to update an entire YAML file.
In practice, there are kinds of problems you can solve with either reusable workflows or a composite workflow. Both approaches have individual strengths and weaknesses. 80% of the time you can probably use either one. But 20% of the time, you’ll need to use one or the other.
For example, if your job needs to run on a specific runner or machine, you need to use reusable workflows. Composite actions don’t specify this type of thing. Composite actions are intended to be more isolated and generic.
Key differences between reusable workflows and composite actions
| Reusable workflows | Composite actions |
| Can connect a maximum of four levels of workflows | Can be nested to have up to 10 composite actions in one workflow |
| Can use secrets | Cannot use secrets |
| Can use if: conditionals | Cannot use if: conditionals |
| Can be stored as normal YAML files in your project | Requires individual folders for each composite action |
| Can use multiple jobs | Cannot use multiple jobs |
| Each step is logged in real-time | Logged as one step even if it contains multiple steps |
With reusable workflows, you can have multiple jobs and that gives you a lot of more granular control—and power. They allow you to specify any number of things and customize them more to your liking.
Reusable workflows also don’t require individual folders for each workflow like composite actions do. This can make using reusable workflows simpler since you can avoid nesting a bunch of different folders like you’d need to do with composite actions.
TL;DR
The more things you can do to follow the DRY principle, the better. Reusable workflows make it simple to spin up new repositories and projects and immediately start using automation and CI/CD workflows with GitHub Actions that you know will work. That saves you time, and it lets you focus more on what’s important: writing great code.
Additional resources
- [Guide] How to build a CI/CD pipeline with GitHub Actions
- [Blog] 10 GitHub Actions resources to bookmark
- [Blog] 7 advanced workflow automation features with GitHub Actions
Tags:
Written by
Related posts

Scaling AI opportunity across the globe: Learnings from GitHub and Andela
Developers connected to Andela share how they’re learning AI tools inside real production workflows.

GitHub for Beginners: Getting started with GitHub Issues and Projects
Learn how to get organized and collaborate more efficiently with this step-by-step tutorial.

7 learnings from Anders Hejlsberg: The architect behind C# and TypeScript
Anders Hejlsberg shares lessons from C# and TypeScript on fast feedback loops, scaling software, open source visibility, and building tools that last.