Unified code-to-cloud artifact risk visibility with Microsoft Defender for Cloud now in public preview
GitHub now makes it easier for teams to track, prioritize, and remediate security risks that matter by connecting code, build artifacts, and production context. Here’s what’s shipped and how you can use these new features:
Linked artifacts with full traceability
Artifacts built through GitHub Actions can now appear in GitHub as “linked artifacts,” even when they’re ultimately stored in external registries such as Azure Container Registry or JFrog Artifactory. For each linked artifact, GitHub shows new metadata: you’ll see what repository built the artifact, which package registry the artifact is stored in, and where it’s been deployed. All attested artifacts are automatically mapped to their source code repositories, so you can trace every artifact back to its origin. This is powered by new Artifact Metadata APIs for storage and deployment records, so your CI/CD workflows or external systems can programmatically send data to GitHub, keeping the linked view up to date.
Runtime risk context in partnership with Microsoft Defender for Cloud
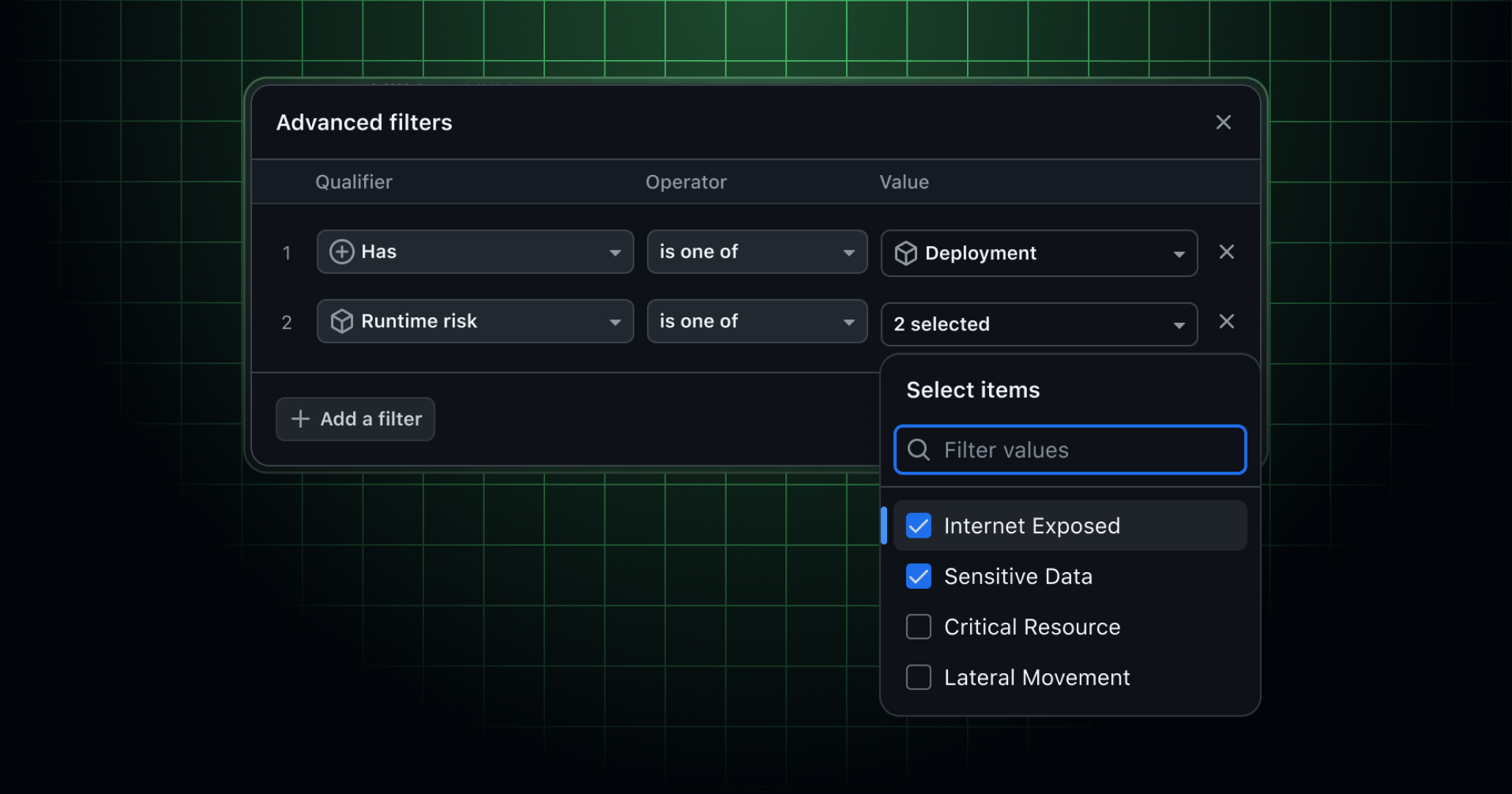
GitHub now shows runtime risk for artifacts, such as whether they are internet-exposed or process sensitive data in production. This context is natively supplied by Microsoft Defender for Cloud, which includes a native implementation of the Deployment Record API to automatically populate deployment records and runtime risk attributes without requiring workflow changes. This gives both security and development teams shared visibility into how build artifacts are being used and the types of real-world risks they may pose once deployed.
Production-aware filtering and campaign targeting
To help teams prioritize the most critical security alerts, GitHub Advanced Security now supports production context filters in Code Scanning, Dependabot, and security campaigns. You’ll find new filter options in the organization-level alert lists and campaign creation flows:
- Filter by registry with
artifact-registry-url: - Filter by deployment status using
has:deployment - Focus on runtime risks with
runtime-risk:(for example,runtime-risk:internet-exposedorruntime-risk:sensitive-data)
With these filters, security and AppSec teams can launch targeted campaigns to remediate the issues that actually affect production, not just theoretical risks. You can assign issues individually or in bulk to Copilot coding agent. Then, the agent will generate draft pull requests with proposed fixes, explaining its reasoning and steps, in order to streamline handoff and reduce manual triage time.
Getting started
- To surface linked artifacts in GitHub, update your build and CI workflows to send artifact metadata using the new APIs (unless you are already using Microsoft Defender for Cloud, in which case container deployments and risk context are handled automatically).
- Use the new filter options in security views to focus triage and campaigns on what’s deployed and exposed.
- Assign critical security issues or campaigns to Copilot coding agent directly from the GitHub issue or campaign view.
These improvements make it possible to focus on and remediate vulnerabilities with real business impact—improving collaboration and visibility for developers, AppSec, and cloud security teams working together on GitHub.
For help or questions, open a discussion in our Community discussion.