Immutable releases are now generally available
GitHub releases now support immutability, adding a new layer of supply chain security. With immutable releases, assets and tags are protected from tampering after publication, so the software you publish—and your users consume—remains secure and trustworthy.
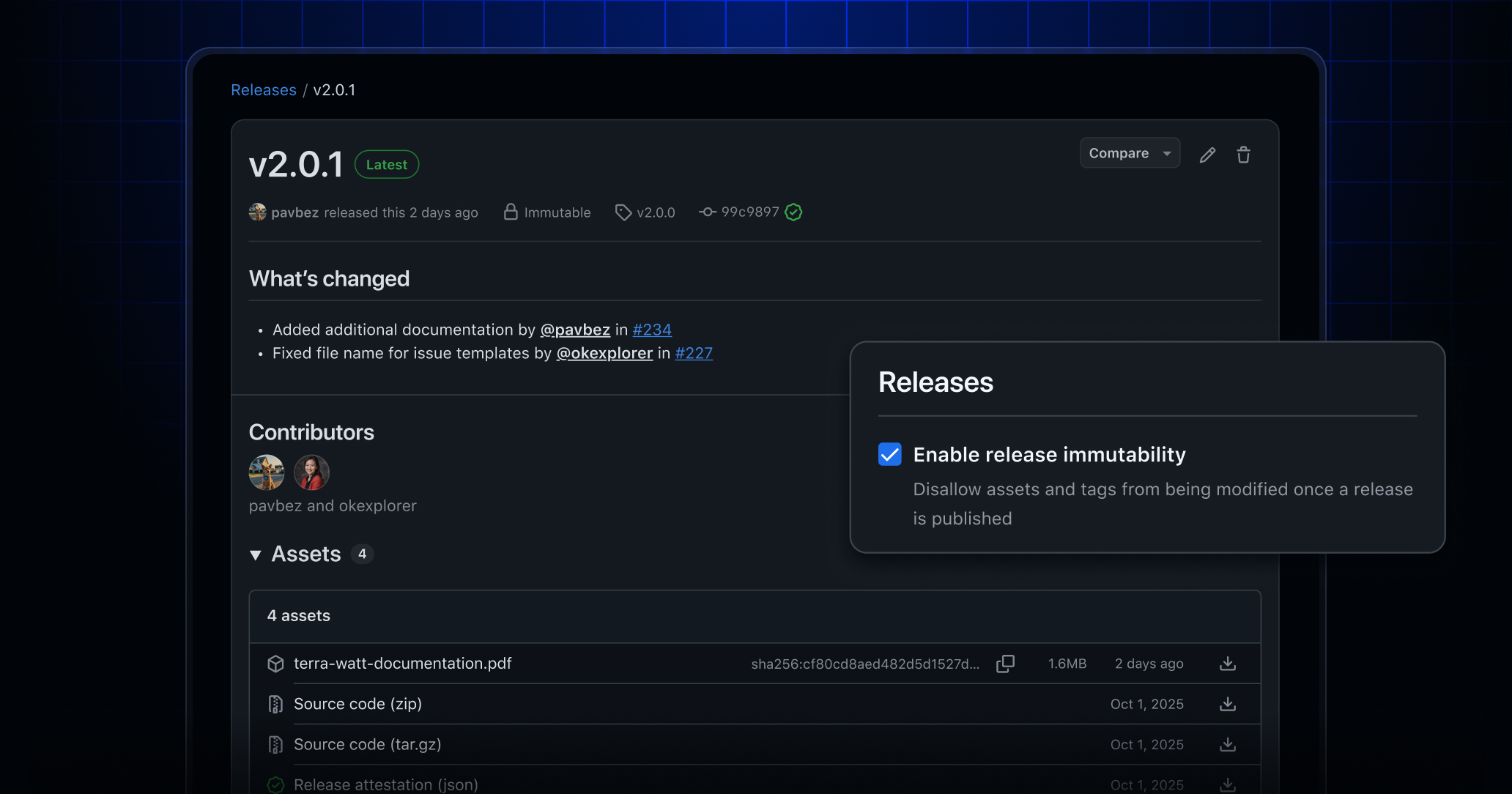
About immutable releases
Immutable releases offer:
- Immutable assets: Once you publish a release as immutable, its assets can’t be added, modified, or deleted. This helps protect distributed artifacts from supply chain attacks.
- Tag protection: Tags for new immutable releases are protected and can’t be deleted or moved.
- Release attestations: Immutable releases receive signed attestations so you can easily verify the authenticity and integrity of assets, both on GitHub and in external environments.
How to enable immutable releases
You can enable immutable releases at the repository or organization level in your settings. Once enabled:
- All new releases are immutable (i.e., assets are locked and tags are protected).
- Existing releases remain mutable unless you republish them.
Disabling immutability doesn’t affect releases created while it was enabled. They remain immutable.
Release attestations and verification
Release attestations let you verify that an artifact is authentic and unchanged, even outside GitHub. Attestations use the Sigstore bundle format, so you can easily verify releases and assets using the GitHub CLI or integrate with any Sigstore-compatible tooling to automate policy enforcement in your CI/CD pipelines. For instructions on how to verify the integrity of a release, see our docs on verifying the integrity of a release.
We’d love your feedback. Share your thoughts and questions on the GitHub Community.
For more information, see our immutable releases documentation.