GitHub brings supply chain security features to the Go community
GitHub’s supply chain security features are now available for Go modules, which will help the Go community discover, report, and prevent security vulnerabilities.

The global Go community embraced GitHub from the beginning—both as a place to collaborate on code and a place to publish packages—leading to Go becoming one of the top 15 programming languages on GitHub today. We’re excited to announce that GitHub’s supply chain security features are now available for Go modules, which will help the Go community discover, report, and prevent security vulnerabilities.
Go was created, in part, to address the problem of managing dependencies in large-scale software. GitHub is the most popular host for open-source Go modules. The features announced today will help not just GitHub users but anyone who depends on GitHub-hosted modules. We are thrilled that GitHub is investing in improvements that benefit the entire Go ecosystem, and we look forward to more collaborations with them in the future.
– Steve Francia, Product Lead: Go Language @ Google
Go modules were introduced in 2019 to make dependency management easier and version information more explicit, and according to the Go Developer Survey 2020 have gained near-universal adoption. Below, I’ll walk you through how each of GitHub’s supply chain security features works with Go modules to improve security for the Go community.
Advisories
GitHub’s Advisory Database is an open database of security advisories focused on high quality, actionable vulnerability information for developers. It’s licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0, so the data can be used anywhere.
So far, we’ve published over 150 existing Go advisories, and this number is growing every day as we curate existing vulnerabilities and triage newly discovered ones.
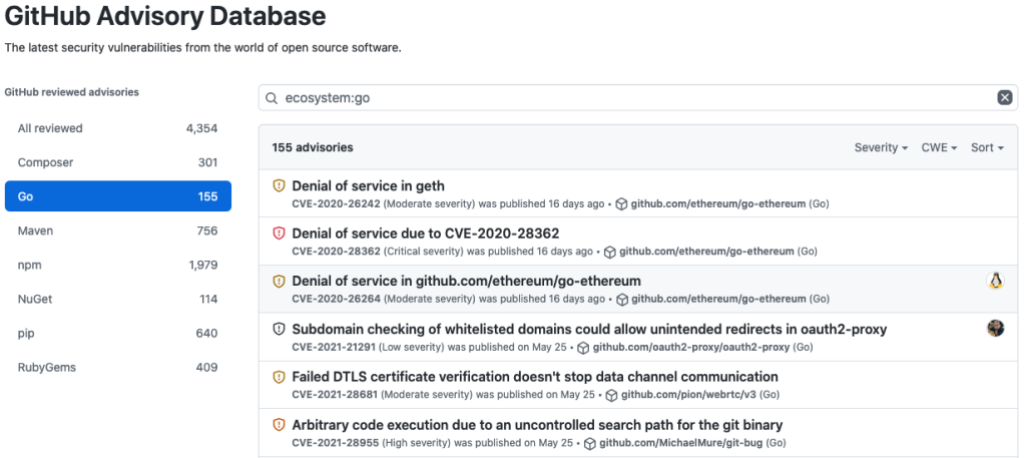
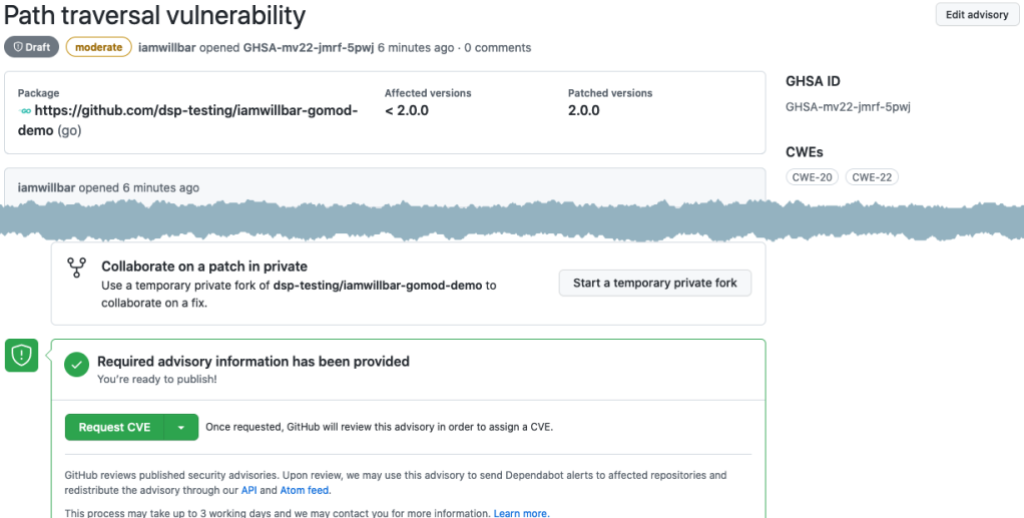
If you’re a Go module maintainer, you can use Security Advisories for coordinated disclosure of vulnerabilities. You can collaborate with vulnerability reporters, such as security researchers, to privately discuss and fix vulnerabilities before announcing them publicly. Security Advisories also make it easy for you to request a Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) identification number for your advisories and to publish them to the National Vulnerability Database (NVD).
Dependency graph
GitHub’s dependency graph analyzes a repository’s go.mod files to understand the repository’s dependencies. Along with security advisories, the dependency graph provides the information needed to alert developers to vulnerable dependencies. To view a repository’s detected dependencies, select the repository’s Insights tab, then select Dependency graph from the sidebar on the left.
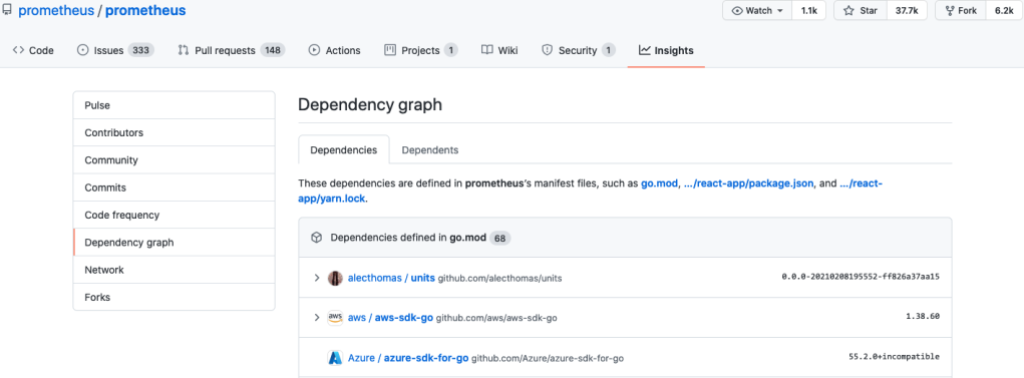
The dependency graph is enabled by default for public repositories, but you must enable it for private repositories. If the dependency graph for your public repository hasn’t already been populated, it will be soon. If you can’t wait you can trigger the update by pushing a change to your go.mod file.
To help prevent new vulnerabilities from being introduced, you can use dependency review to see the impact of changes to your go.mod files when reviewing pull requests.
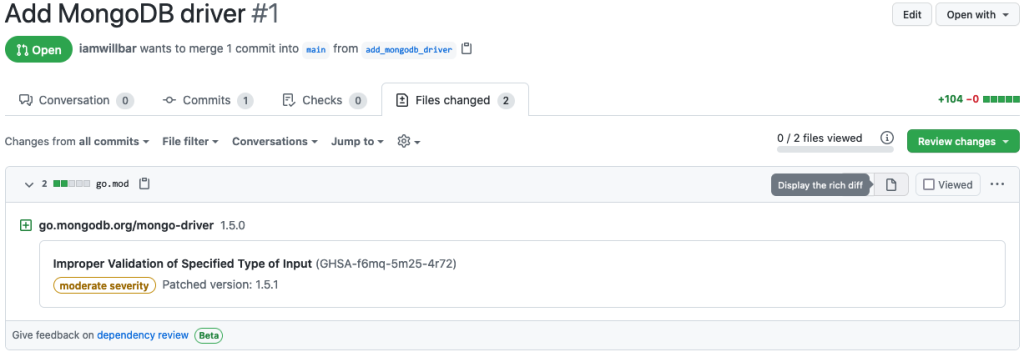
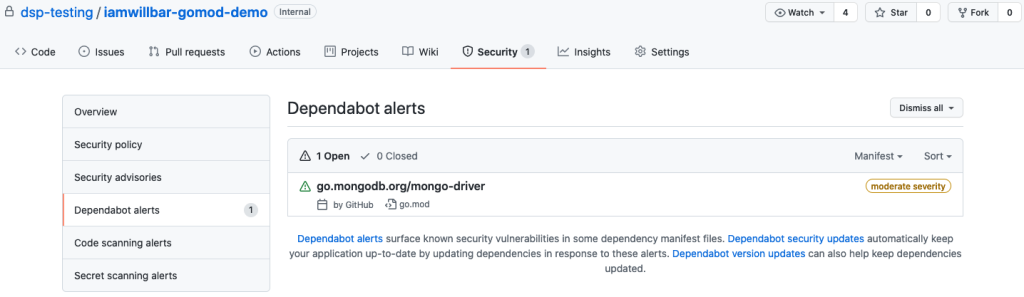
Dependabot alerts
Dependabot alerts notify you when new vulnerabilities are discovered in Go modules you’re already using. You can use our new notification configuration to fine-tune which notifications you receive.
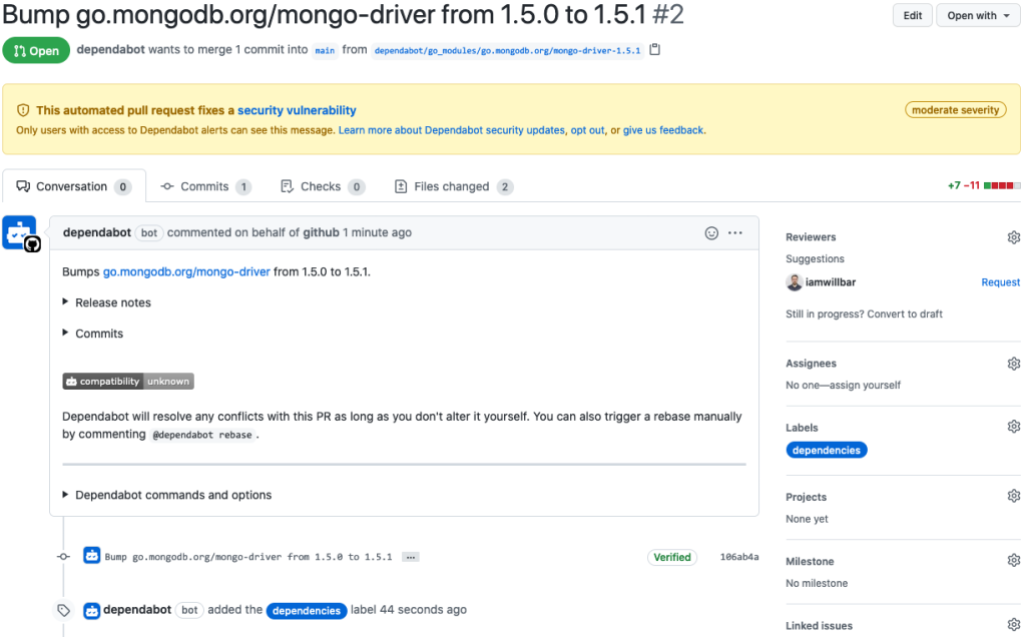
Dependabot security updates
What’s better than being alerted to a vulnerable dependency? Getting a pull request that automatically upgrades your vulnerable Go modules to a version without the vulnerability! That’s exactly what Dependabot security updates do.
We’ve found that repositories that automatically generate pull requests to update vulnerable dependencies patch their software 40% faster than those who don’t.
Get started and learn more
Get started today by securing your Go repository, or learn more about each of GitHub’s supply chain security features:
Tags:
Written by
Related posts

AI-supported vulnerability triage with the GitHub Security Lab Taskflow Agent
Learn how we are using the newly released GitHub Security Lab Taskflow Agent to triage categories of vulnerabilities in GitHub Actions and JavaScript projects.

Community-powered security with AI: an open source framework for security research
Announcing GitHub Security Lab Taskflow Agent, an open source and collaborative framework for security research with AI.

Bugs that survive the heat of continuous fuzzing
Learn why some long-enrolled OSS-Fuzz projects still contain vulnerabilities and how you can find them.