Performance Impact of Removing OOBGC
Until last week, GitHub used an Out of Band Garbage Collector (OOBGC) in production. Since removing it, we decreased CPU time across our production machines by 10%. Let’s talk about…
Until last week, GitHub used an Out of Band Garbage Collector (OOBGC) in production. Since removing it, we decreased CPU time across our production machines by 10%. Let’s talk about what an OOBGC is, when to use it, and when not to use it. Then follow up with some statistics about the impact of removing it from GitHub’s stack.
What is an Out of Band Garbage Collector?
An OOBGC is not really a Garbage Collector, but more of a technique to use when deciding when to collect garbage in your program. Instead of allowing the GC to run normally, the GC is stopped before processing a web request, then restarted after the response has been sent to the client. Meaning that garbage collection occurs “out of band” of request and response processing.
When to use an Out of Band Garbage Collector
Ruby’s GC is a “stop the world, mark and sweep” collector. Which means that when the GC runs, your program pauses, and when the GC finishes your program resumes. The time your program is paused is called “pause time”, and while your program is paused it can’t do anything. Historically, Ruby’s GC would pause the program for long periods of time. We would rather clients don’t wait around for the GC to run, so only executing GC after each request made sense.
When not to use an Out of Band Garbage Collector
In the past years, Ruby’s Garbage Collector has undergone many performance improvements. These changes include: becoming a generational collector, incremental marking, and lazy sweeping. A generational collector reduces the overall amount of work the GC needs to do. Incremental marking and lazy sweeping mean that the GC can execute concurrently with your program. What these techniques add up to is less time spent in GC, and higher throughput of your program.
Since the OOBGC runs the GC after the response is finished, it can cause the web worker to take longer in order to be ready to process the next incoming request. This means that clients can suffer from latency due to queuing wait times.
If a particular request doesn’t allocate enough garbage to warrant a GC execution under normal conditions, then the OOBGC could cause the process to do more work than it would have without the OOBGC.
Finally, the OOBGC can cause full collections (examining old and new objects) which defeats the generational GC optimizations.
GitHub has been using Ruby in production for a long time, and at the time adding an OOBGC made sense and worked well. However, it is always good to question assumptions, especially after technological advancements such as the improvements made in Ruby’s GC. We wanted to see if running an OOBGC was still necessary for our application after upgrading to Ruby 2.4, so we decided to remove it and observe the impact.
Impact of removing the OOBGC
After removing the OOBGC, we saw a 10% drop in Kubernetes cluster CPU utilization:

This graph compares cluster CPU utilization from the current day, previous day, and previous week:

The blue line is CPU utilization for the day the patch went out. You can see a great drop around 15:20.
This graph shows the difference in core utilization before and after OOBGC removal. In other words “number of cores used yesterday” minus “number of cores used today”:

We saw a savings of between 400 and around 1000 cores depending on usage at that point in the day.
Finally, removing OOBGC reduced average response times by about 25% (the gray line is with OOBGC, the blue line is without):

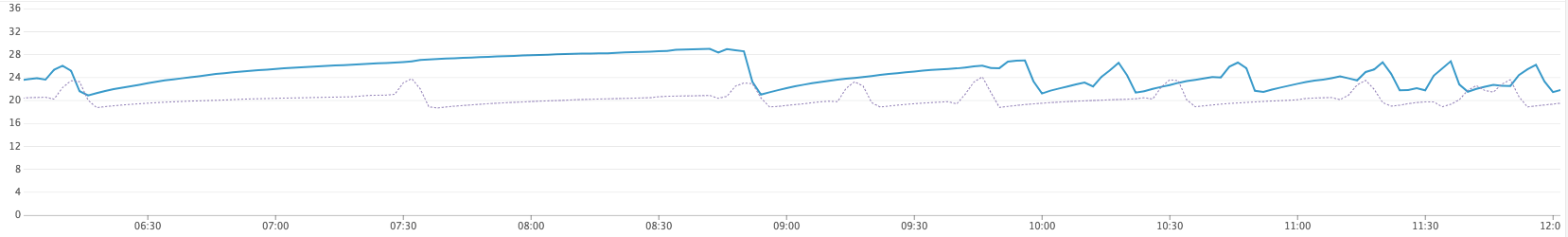
Of course, removing OOBGC was not an all around win. Incremental marking and lazy sweeping amortize the cost of memory collection over time. This means that memory usage will increase on average, and that is what we observed in production:
Conclusion
For our application, the CPU savings far outdid the price we had to pay in average memory usage. Removing the OOBGC from our system resulted in a great savings for our systems. Taking measurements, acting on data, and questioning assumptions is one of the most difficult and fun parts of being an engineer. This time it paid off for us, and hopefully this post can help you too!
Written by
Related posts

GitHub availability report: January 2026
In January, we experienced two incidents that resulted in degraded performance across GitHub services.

Pick your agent: Use Claude and Codex on Agent HQ
Claude by Anthropic and OpenAI Codex are now available in public preview on GitHub and VS Code with a Copilot Pro+ or Copilot Enterprise subscription. Here’s what you need to know and how to get started today.

What the fastest-growing tools reveal about how software is being built
What languages are growing fastest, and why? What about the projects that people are interested in the most? Where are new developers cutting their teeth? Let’s take a look at Octoverse data to find out.