Archiving repositories
Just because a repository isn’t actively developed anymore and you don’t want to accept additional contributions doesn’t mean you want to delete it. Now archive repositories on GitHub to make…

Just because a repository isn’t actively developed anymore and you don’t want to accept additional contributions doesn’t mean you want to delete it. Now archive repositories on GitHub to make them read-only.
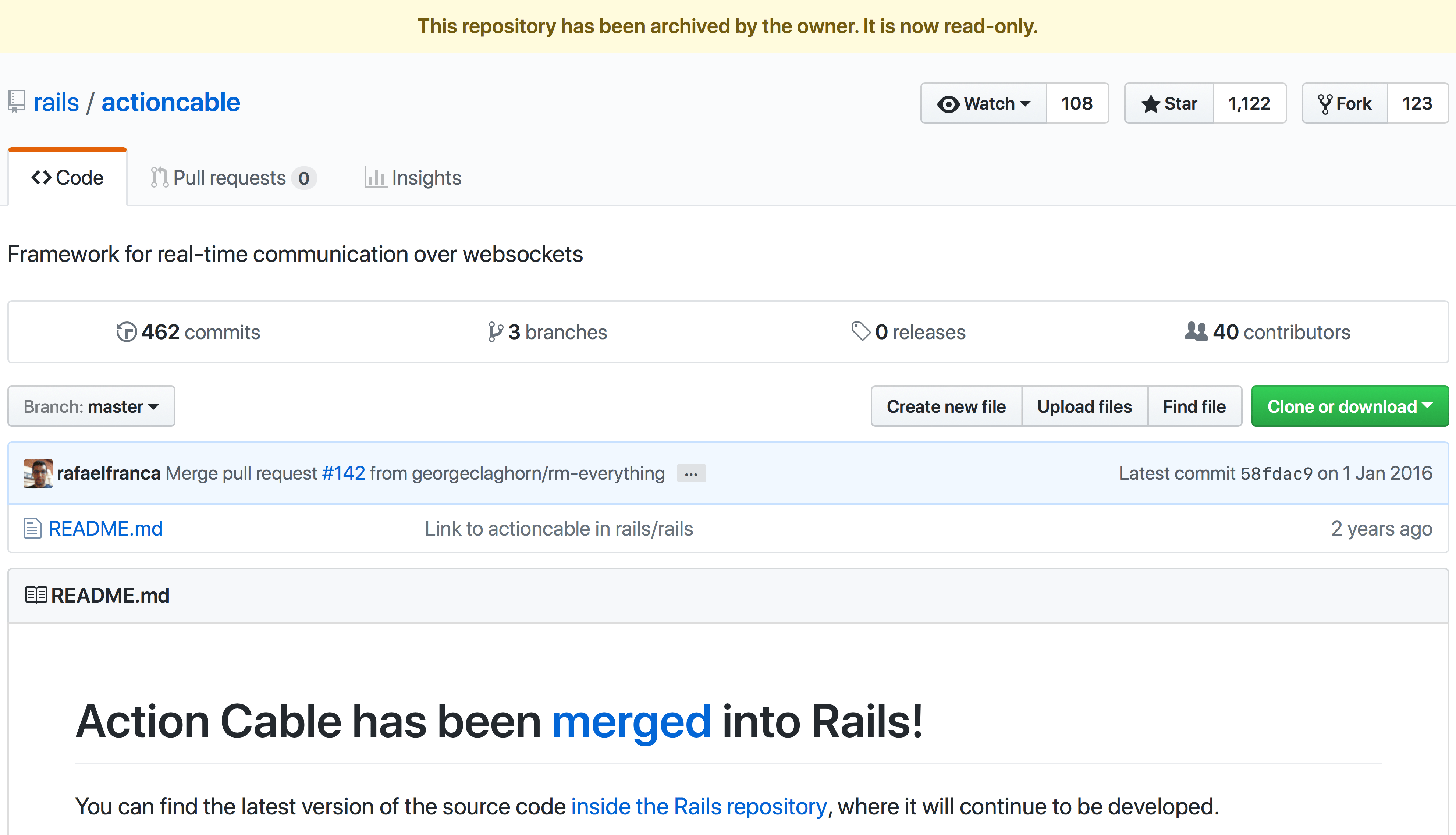
Archiving a repository makes it read-only to everyone (including repository owners). This includes editing the repository, issues, pull requests, labels, milestones, projects, wiki, releases, commits, tags, branches, reactions and comments. No one can create new issues, pull requests, or comments on an archived repository, but you can still fork archived repositories—allowing development to continue elsewhere for archived open source projects.
To archive a repository, go to your Repository Settings Page and click Archive this repository.
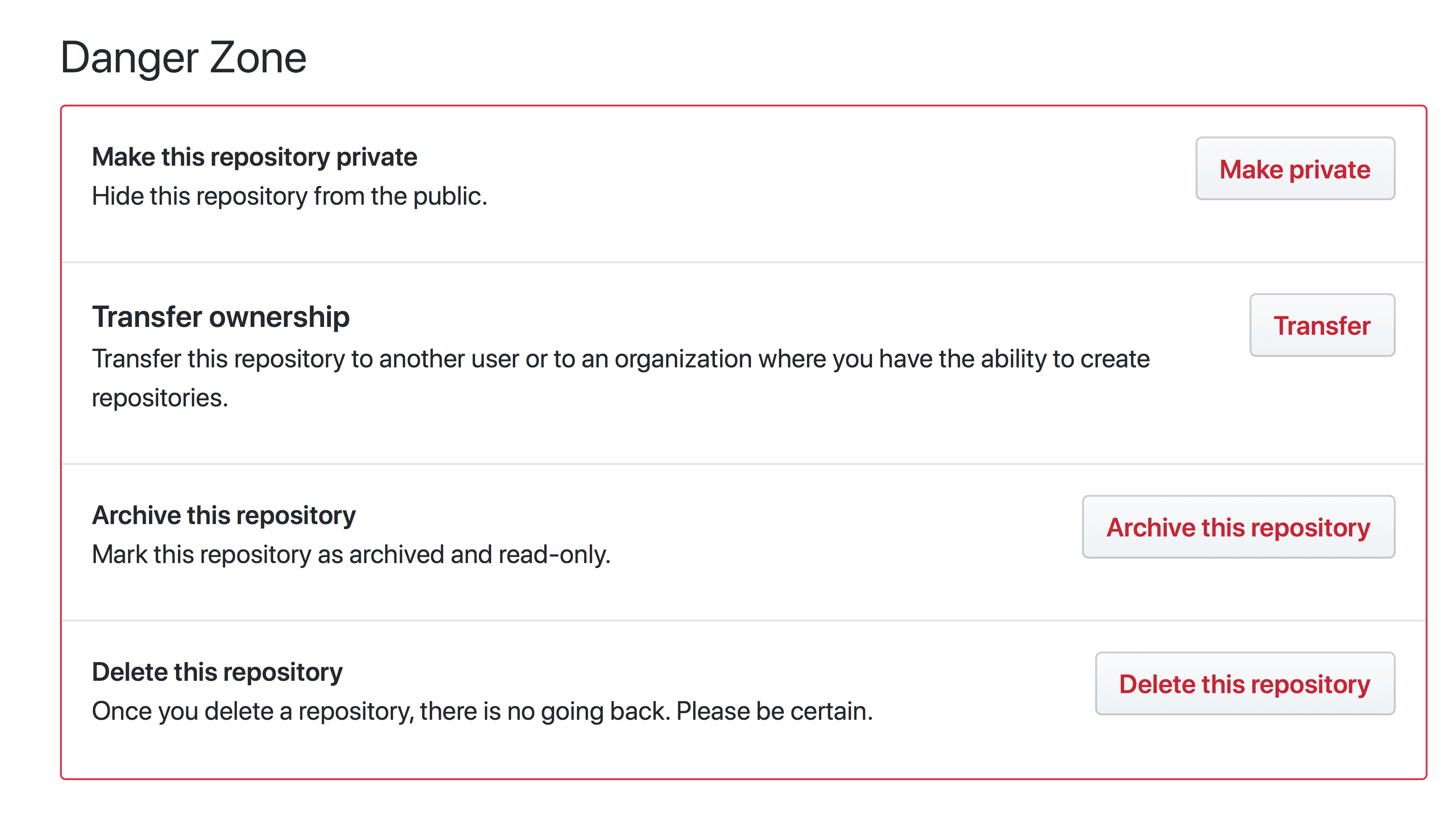
Before archiving your repository, make sure you’ve changed its settings and consider closing all open issues and pull requests. You should also update your README and description to make it clear to visitors that it’s no longer possible to contribute.
If you change your mind and want to unarchive your repository, click Unarchive this repository in the same place. Please note that most archived repository settings are hidden and you’ll have to unarchive the repository to change them.
To learn more, check out the documentation on archiving repositories. Happy archiving!
Written by
Related posts

GitHub availability report: January 2026
In January, we experienced two incidents that resulted in degraded performance across GitHub services.

Pick your agent: Use Claude and Codex on Agent HQ
Claude by Anthropic and OpenAI Codex are now available in public preview on GitHub and VS Code with a Copilot Pro+ or Copilot Enterprise subscription. Here’s what you need to know and how to get started today.

What the fastest-growing tools reveal about how software is being built
What languages are growing fastest, and why? What about the projects that people are interested in the most? Where are new developers cutting their teeth? Let’s take a look at Octoverse data to find out.