octocatalog-diff: GitHub’s Puppet development and testing tool
Today we are announcing the open source release of octocatalog-diff: GitHub’s Puppet development and testing tool. GitHub uses Puppet to configure the infrastructure that powers GitHub.com, comprised of hundreds of…
Today we are announcing the open source release of octocatalog-diff: GitHub’s Puppet development and testing tool.
GitHub uses Puppet to configure the infrastructure that powers GitHub.com, comprised of hundreds of roles deployed on thousands of nodes. Each change to Puppet code must be validated to ensure not only that it serves the intended purpose for the role at hand, but also to avoid causing unexpected side effects on other roles. GitHub employs automated Continuous Integration testing and manual deployment testing for Puppet code changes, but it can be time-consuming to complete the manual deployment testing across hundreds of roles.
Recently, GitHub has been using an internally-developed tool called octocatalog-diff to help reduce the time required for these testing cycles. With this tool, developers are able to preview the effects of their change across all roles via a distributed “catalog difference” test that takes less than three minutes to run. Because of reduced testing cycles and increased confidence in their deployments, developers can iterate much faster on their Puppet code changes.
Before demonstrating octocatalog-diff, let’s address the existing solutions and the reasoning for creating a new tool.
Existing landscape of Puppet testing
There are three main strategies for Puppet code testing in wide use, and GitHub uses all of them:
-
Deployment testing — actually running the Puppet agent (possibly with
--noopto preview actions without actually making changes) allows the developer to review log files or examine the system to see if the results are as intended. -
Automated testing — this may include unit tests with
rspec-puppet, acceptance tests withbeaker, syntax checkingpuppet parser validateor linting withpuppet-lint. These types of tests often run in a Continuous Integration environment to verify that the code meets a set of specified criteria. -
Catalog testing —
octocatalog-diffand Puppet’scatalog_previewmodule both allow comparison of catalogs produced by two different Puppet versions or between two environments.
GitHub needed a catalog testing approach that could run from a development or CI environment, because for security reasons only a small number of engineers have direct access to the Puppet master. Because catalog_preview is designed to be fully integrated into the Puppet master, it would be inaccessible for a large portion of GitHub’s Puppet contributors, and as such it was not the right fit. Therefore, we embarked upon our own development of a tool that could run independently of a Puppet installation, and produced octocatalog-diff.
octocatalog-diff
This screen shot shows octocatalog-diff in action, as run from a developer’s workstation:
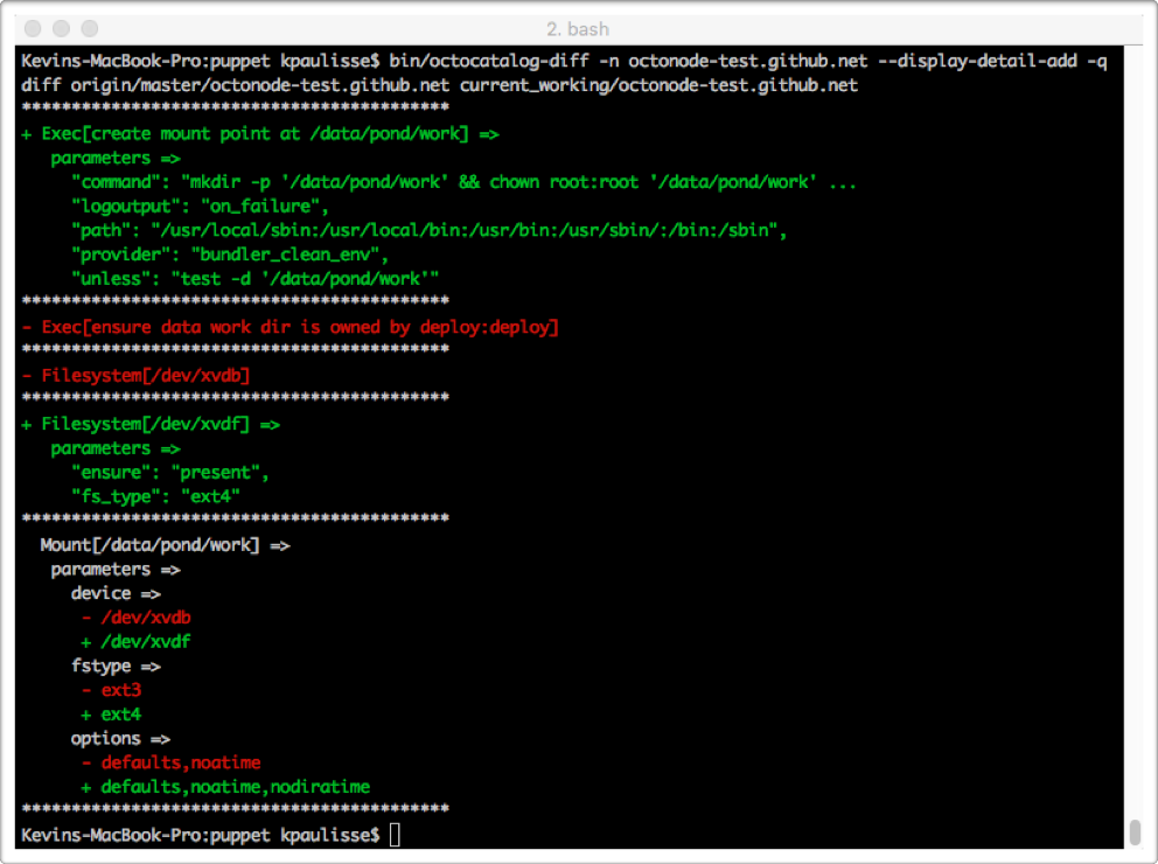
In this example, the developer is comparing the Puppet catalog changes between the master branch and the Puppet code in the current working directory. Two resources are being created (an Exec resource to create the mount point, and a Filesystem resource to format /dev/xvdf). Two resources are being removed (the old Exec resource to change permissions on the work directory, and the old Filesystem on /dev/xvdb). And one resource is being changed (several parameters of the mount point are being updated).
The output was generated in under 15 seconds, obviating a traditional workflow of committing code, waiting for CI jobs to pass, deploying code to a node, and reviewing the results. The process that generated this output did not require access to, or put any load on, either the Puppet master or the node whose catalog was computed.
The next graphic shows output from octocatalog-diff when run via a distributed CI job, to preview the effects of a code change on nodes across the fleet:
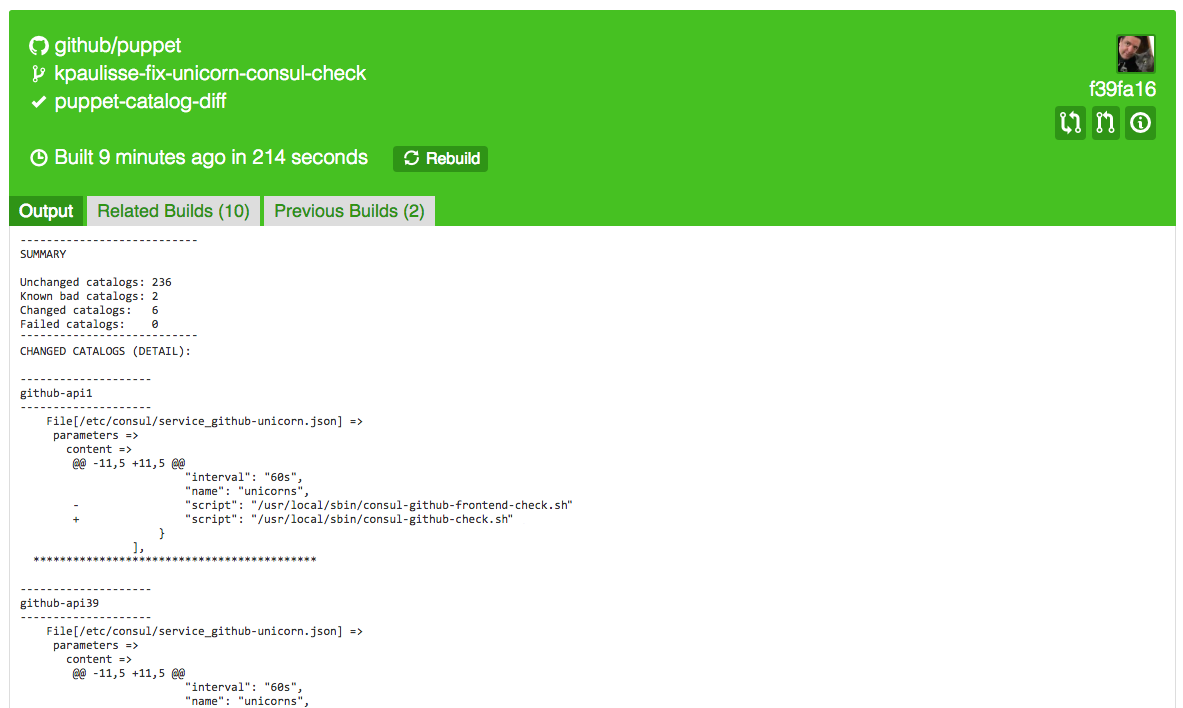
In this example, the developer wishes to see which systems will be affected by a particular change to the Puppet code. The output from octocatalog-diff reveals that the changes affect certain GitHub API nodes. The developer can use this information to test deployment on just those six representative systems instead of hundreds or thousands of nodes. This cuts down on unnecessary testing and provides confidence that there will not be unexpected side effects, allowing the developer to complete the work more efficiently and with less risk.
octocatalog-diff key features
octocatalog-diff has several useful features:
- Comparing catalogs generated by two branches of a Git repository
- Predicting differences due to fact changes by allowing the developer to override facts
- Comparing the content differences of static files, not just the path differences
- Caching base catalogs to allow subsequent runs to complete faster
- Ignoring selected types, titles, or parameters to suppress meaningless or known changes
octocatalog-diff is able to compare catalogs obtained in the following ways:
- Compiling a catalog from Puppet code (the most common use case)
- Reading in a JSON file containing a compiled catalog
- Retrieving the last known catalog for a node from PuppetDB
- Querying the Puppet master server for the catalog via its API
octocatalog-diff at GitHub
octocatalog-diff is being used in “catalog only” mode as a Continuous Integration (CI) job in GitHub’s Puppet repository. Upon every push, octocatalog-diff compiles the catalogs for over 50 critical roles, using real node names and facts, to ensure that changes to one role do not unexpectedly break Puppet catalogs for other roles. In addition, developers use octocatalog-diff in “difference” mode to preview their changes across the fleet, which has enabled them to perform major refactoring with minimal risk.
Over the past year, GitHub has successfully upgraded from Puppet 3.4 to 4.5, migrated hard-coded parameters from thousands of manifests into the hiera hierarchical data store, transitioned node classification from hostname regular expressions to application and roles, expanded roles to run in different environments and in containers, and upgraded roles to run under new operating systems. Using octocatalog-diff to predict changes across the fleet, a relatively small number of developers accomplished these substantial initiatives quickly and without their Puppet changes causing outages.
Open source
octocatalog-diff is released to the open source community under the MIT license.
While we find octocatalog-diff to be reliable for our needs, there are undoubtedly configurations or customizations within others’ Puppet code bases that we have not anticipated. We welcome community participation and contributions, and look forward to enhancing the compatibility and functionality of the tool.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge and thank the Site Reliability Engineering team at GitHub for their suggestions and code reviews, and the other engineers at GitHub who worked patiently with us to diagnose problems and test improvements during the pre-production stages.
Written by
Related posts

GitHub availability report: February 2026
In February, we experienced six incidents that resulted in degraded performance across GitHub services.
Addressing GitHub’s recent availability issues
GitHub recently experienced several availability incidents. We understand the impact these outages have on our customers and are sharing details on the stabilization work we’re prioritizing right now.

GitHub availability report: January 2026
In January, we experienced two incidents that resulted in degraded performance across GitHub services.