Recent Services Interruptions
Here’s a summary of the outages we encountered this week and what we’re doing to prevent this from happening again. Monday January 3rd Monday marked the first “real” workday for…
Here’s a summary of the outages we encountered this week and what we’re doing
to prevent this from happening again.
Monday January 3rd
Monday marked the first “real” workday for most people in 2011. Our wonderful
users all hopped online and got back to hacking. As North American work hours
came around our Pacemaker application failed over one of our xen machines which
happened to host our primary load balancer. This is something that happens
really rarely and most of our users notice because the load balancer is the
machine that everyone hits when accessing GitHub. This exposed a few problems in our
infrastructure that we’ll be addressing.
Our internal routing had issues that we hadn’t experienced before due to our
growing internal network. We specifically had problems with internal DNS
resolution after the failover as well as routing certain traffic to some of our
frontend machines.
New Relic was great in helping us diagnose this issue.

Something was taking WAY too long compared to how things normally look.
Everything was essentially timing out.
Unfortunately it took us a little while to figure out the real issues were with
networking. We know this can happen now and the team has a much better
understanding over the networking overall.
We’re now aware that under our current configuration, certain services on our load balancers must be located on different hosts to prevent this particular routing issue. We have a plan in place to reconfigure that part of our networking setup to remove the issue. In the meantime, we’re also setting up a third load balancer to restore our n+1 redundancy.
During all of the networking insanity we had a fileserver, fs7, failover during
this bumpy outage. We use a high availability setup for the fileservers, and
they fail over a lot more often than you’d think. We kind of chalked it up to
general insanity inside the cluster and our trusty sysadmin, Tim, went off to
make sure we didn’t have another day like Monday.
We had intermittent service between 8:30AM PST and about 3PM PST.
Tuesday January 4th
Around 7AM PST on Tuesday we started to notice high load and an abnormally high
number of http connections. By 8AM fs7, the same machine with problems the
previous day, had failed over. The failover machine is usually online within a
few minutes but due to the high load it hobbled along for a little over an
hour. Shortly after that it kernel panicked which required Tim to spend some
quality time with it. We realized that the kernel the failed fileserver was
running was older than most of the rest of our fileservers so we decided to
upgrade it. This took us a little bit and service was restored on fs7 by 3PM
PST. Keep in mind that this only impacted a subset of our customers but a
second shaky day obviously isn’t what we want for our users.
Everything was back to normal but two straight days of issues impacting one
fileserver left us a little spooked and focusing hard on what was wrong with
fs7 specifically. Everything seemed to corrolate around north american
business hours starting in EST, so we camped out and waited for wednesday
morning.
Wednesday January 5th
Wednesday we saw the heightened load start around 5AM PST and resulted in a
bumpy two hours. The system went in and out of swap before swapping itself to
death shortly after 7am PST.
06:58:01 AM kbmemfree kbmemused %memused kbbuffers kbcached kbswpfree kbswpused %swpused kbswpcad
07:10:01 AM 124428 16347368 99.24 1195892 7180972 1036700 11868 1.13 8
07:11:01 AM 90832 16380964 99.45 865808 4479240 1036700 11868 1.13 8
07:12:01 AM 96648 16375148 99.41 205644 939236 1036676 11892 1.13 36
07:13:10 AM 81588 16390208 99.50 36040 104276 0 1048568 100.00 9632
07:14:10 AM 83004 16388792 99.50 29232 100256 0 1048568 100.00 3812
07:15:10 AM 81992 16389804 99.50 2324 67620 0 1048568 100.00 3212You can see it die off in collectd graphs.
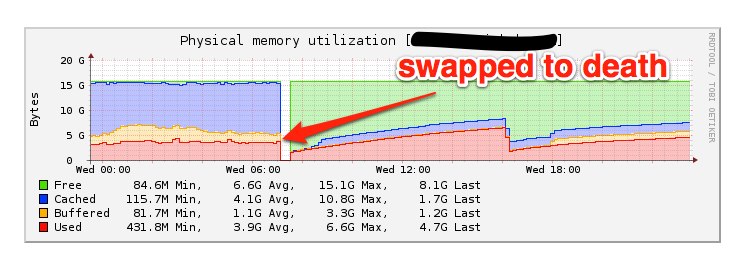
Once again fs7 failed over and this time it had a lot of queued requests to
handle when the failover was promoted. As the failover came up its load stayed
extremely high but started to settle after 20-30 minutes of hammering it. We
were unhappy that it happened again, but we were glad that we’d avoided
another prolonged outage.
Around 8:30AM PST we saw another burst of activity on the fileserver, luckily
we were watching the system closely and kept the system in check. You can see
the memory start to rise here.
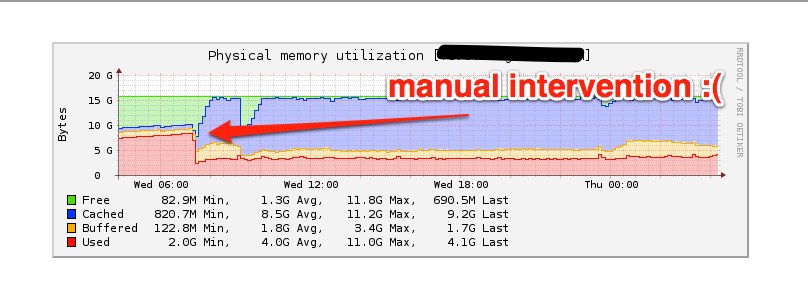
We noticed something happening on the system that never should though, dozens
of ‘git pack-objects’ calls running. Normally Librato keeps these processes in
check but something seemed to be ignoring this. We made it through the second
onslaught and had time to really dig into what might be causing the issue.
We started looking into what networks were on the fileserver, I’m sure you
recognize a few of them.
We were investigating whether or not this specific fileserver might be
overloaded due to popular projects when something else popped up. Joe from
Librato pointed us to some really awkward behavior we were seeing in system
resource usage on the server. Something that we weren’t managing with Librato
really grew out of control during the times we saw service interruptions and
high load.

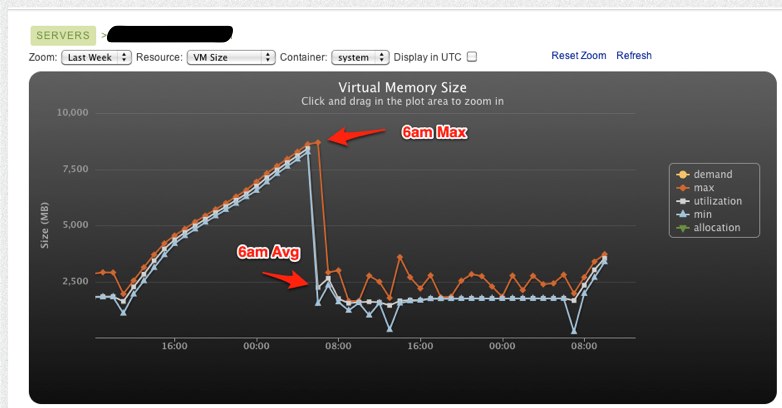
Memory grew linearly from around 3PM PST the day before until 5am where it
maxed out and eventually lead to the box swapping itself to death.
You can also see the virtual memory follow a similar trend here.
With this information we were able to quickly identify that the git-http
service that’s running on the fs servers was not under Librato’s policy
management. We’ve been slowly pushing more and more people to use git-http by
default and we hadn’t experienced such a spike in traffic as we’ve seen over
the past few days. We put git-http into a Librato container and we had to wait
for Thursday morning to really test it.
Problem Solved
This morning went smoothly. Librato kept all of our git-http processes in
check despite another morning of enormous git-http traffic. We’re excited to
get back to work on making GitHub better, not keeping GitHub running. We’re
really sorry for any inconvenience our users experienced due to the insanity
over the past few days. We hope this run down of the events gives our users
some insight into how we handle problems. Having metrics around as many things
as possible really helped us identify a difficult problem to diagnose.
A big thanks go out to Saj from Anchor for waking up in the middle of the night for three days straight to help us out with systems issues. Thanks to Joseph Ruscio for the Librato insight that revealed the real fix.
Written by
Related posts

From pair to peer programmer: Our vision for agentic workflows in GitHub Copilot
AI agents in GitHub Copilot don’t just assist developers but actively solve problems through multi-step reasoning and execution. Here’s what that means.

GitHub Availability Report: May 2025
In May, we experienced three incidents that resulted in degraded performance across GitHub services.

GitHub Universe 2025: Here’s what’s in store at this year’s developer wonderland
Sharpen your skills, test out new tools, and connect with people who build like you.